DIABETIC RETINOPATHY
The health complications arising from diabetes affect many parts and systems in your body, and the eyes are no exception. Diabetic retinopathy affects the blood vessels in your eyes, at the surface of focus, the retina.
Left untreated, diabetic retinopathy can lead to blindness, so book a consultation with the eye care professionals at the Witlin Center for Advanced Eye Care, serving East Brunswick, and Toms River, New Jersey. Call us for an appointment today.
What is diabetic retinopathy?
What complications can diabetic retinopathy create?
How is diabetic retinopathy treated?
Witlin Center for Advanced Eye Care
Working Hours
MONDAY
8:30 AM – 4:00 PM
TUESDAY
8:30 AM – 4:00 PM
WEDNESDAY
8:30 AM – 4:00 PM
THURSDAY
8:30 AM – 4:00 PM
FRIDAY
8:30 AM – 3:00 PM
SAT / SUN
CLOSED
Locations
Years of Clinical Experience
Eye Surgical Procedures
BOOK APPOINTMENT
CUSTOMER REVIEWS
Dr Desai was great! He made me feel comfortable about the entire procedure. Dr Desi and his staff followed up with me later that day, the next day and a few days after the procedure. The location in somerset that he uses is very clean and the staff there is excellent as well. My husband was in the waiting area and they updated him to assure him that everything was going according to schedule and the procedure was going well. I would highly recommend Witlin for the Doctors as well as procedures and eye care.
G White
Dr. Desai provided me with the highest level of service I have experienced from any physician to date. He took a considerable amount of time to explain my diagnosis and treatment options. There was no rush to his bedside manner. Even after my surgery (which went perfectly), he was available for any questions or concerns I had. I would (and have) recommend Dr. Desai to family and friends.
Hemlata Shah
OUR SERVICES

GLAUCOMA |
ASTIGMATISM |
CATARACTS |
KERATOCONUS |

LASER EYE SURGERY |
LASIK SURGERY |

MACULAR DEGENERATION |

CORNEAL TRANSPLANT |
PRK |
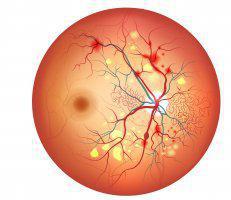
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY |
PTERYGIUM SURGERY |

DRY EYES |

FUCHS DYSTROPHY |
CLEAR LENS EXCHANGE |

LIPIFLOW |

MULTIFOCAL |
PINK EYE |

EMERGENCY EYE CARE |

RED EYES |

EYE FLOATERS |

